Up next
Kate Shemirani: Vaccine Injury Update & Natural, God-given Solutions
Biden Halts Natural Gas Leases In Insane Move During Russian Energy Crisis
Natural Disasters To Watch Out For In The Future
FULL SHOW: Biden Support COLLAPSES, Trump WINS Immunity Case, Jill Biden's CRINGE Pep Talk, And More
BREAKING! What the Media is MISSING in the Trump PresidentialI Immunity Ruling! Viva Frei Vlawg
Presidential Immunity And More Debate Fallout | 538 Politics Podcast
'No kings in America': Biden criticises supreme court decision on presidential immunity
Judge Jeanine Pirro reacts to SCOTUS ruling on presidential immunity.
Why SCOTUS Is Saving Trump Immunity for Last
SCOTUS Leaves Immunity Hanging! Rebel News SHOCKS Canadian PMs? Trump vs. Nipple Judge & MORE!
FLASHBACK: Hillary Clinton's Lawyer DELETED 33k Emails; GRANTED IMMUNITY!
Did Biden RETALIATE against Texas with liquid natural gas ban?
KZN Floods | Discussion | Ways to minimise the damage from natural disasters
Trump Compares Himself to VIOLENT ROGUE COP - Campaigns on Immunity & Limitless Power!!!
The Natural Liver Cleanser: Apple Cider Vinegar and Lemon Water
Violent threats explode, Trump lawyer says immunity for assassination 1/10/24 TDPS Podcast
Washington Today (1-9-24): Federal Appeals Court hears Donald Trump's claim of presidential immunity
Timcast IRL - Ray Epps WINS, Gets NO JAIL TIME, Trump Team Argues Immunity Appeal w/Trent Staggs
HE'S GONE!!! Trump Posts Most INSANE VIDEO to Truth Social RAMBLING About Immunity!
Trump speaks following hearing on immunity in election interference case
Biotic and abiotic factors in Earth’s natural systems | High school biology | Khan Academy
BUILDING OF TENNESSEE GAS PIPELINE TO OAK RIDGE GARDNER DENVER CO. NATURAL GAS 90644
Why Cheating is Natural To Men
EXPLOSIVE NIGHT OF DESTRUCTION*NATURAL HEALTH & HEALING ALTERNATIVES*AWAKENING ZOMBIES*
Natural Ozempic alternatives that don't come with side effects #drberg #weightloss #keto #fasting
Losing Hair? Going Bald? Can it Really be Stopped?–Natural and Medical Methods | Trailer
Eugenia Cheng: I’m More Afraid of Natural Stupidity Than AI!
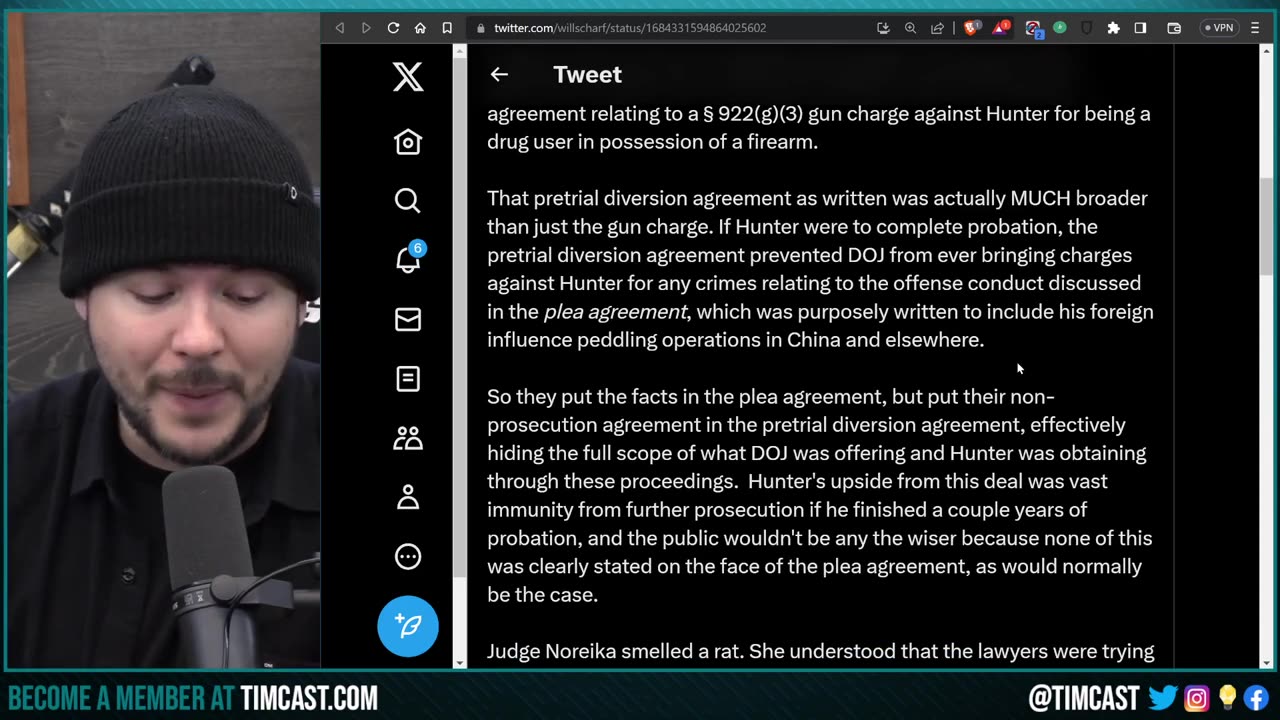
Report: Mark Meadows granted immunity deal in Trump’s federal election interference case
OH NO: Mark Meadows FLIPS on Trump, granted immunity! #shorts
OH NO: Mark Meadows FLIPS on Trump, granted immunity!
Extreme Natural Phenomena | Science pills
“NATURAL GAS” 1930 NATURAL GAS PRODUCTION AND PIPELINE CONSTRUCTION DOCUMENTARY 91494
Will SCOTUS Confer Immunity to Donald Trump? Should It?
The Great Barrier Reef: The Story of a Natural Wonder | Science pills
La Gran Barrera de Coral: historia de una maravilla natural | Píldoras de ciencia
4 Natural Bodybuilders vs 2 Fakes | HasanAbi Reacts
UFC Champ Exposes Maui Fire Land Conspiracy On LIVE TV: "These Fires Are NOT Natural"
If Trump dies of natural causes, they'll say he was killed
Natural immunity wins
" NEW ZEALAND TODAY” EARLY 1960s EDUCATIONAL FILM AUCKLAND NATURAL RESOURCES & INDUSTRY 91334
"Vivek and Trump Are Natural Leaders, but He's Not Ready Yet!" - Sailor John BLASTS Vivek
RFK Jr. AGAINST Ending Qualified Immunity
Natural immunity
Past SARS-CoV-2 infection protection against re-infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(22)02465-5/fulltext Group 1 Past SARS-CoV-2 infection Group 2 No past SARS-CoV-2 infection Effectiveness of past infection by outcome Infection Symptomatic disease Severe disease Findings High levels of protection from infection caused by Alpha, beta, and delta variants Lower levels of protection from infection caused by Omicron BA.1 variant Effectiveness against re-infection with the omicron BA.1 variant Protection against reinfection, 45·3% Protection against omicron BA.1 symptomatic reinfection, 44% Protection against severe disease if reinfected with BA.1 is 88.9% Protection from re-infection with ancestral strains Alpha and delta variants Declined over time 78·6% at 40 weeks Protection against re-infection with omicron BA.1 Declined more rapidly 36·1% at 40 weeks Protection against severe disease at 40 weeks if reinfected Remained high for all variants 90·2% for alpha and delta variants 88·9% for omicron BA.1 Data suggests that the level of protection afforded by previous infection is at least as high, if not higher than that provided by two-dose vaccination using high-quality mRNA vaccines As of June 1, 2022 COVID-19 pandemic had caused an estimated 17·2 million total deaths 6·88 million reported deaths 7·63 billion total infections and re-infections. Between 15th November 2021 and 1st June 2022 3·8 billion people 46% of the global population, have been infected by omicron and sublineages. Understanding needed for Predicting future potential disease burden Designing policies, travel, access to venues Informing choices, vaccines Estimate protection from past infection Systematically synthesise studies 65 studies from 19 countries By variant By time since infection Up to Sept 31, 2022
- Top Comments
- Latest comments